Vulnerability Scanners Work
Vulnerability scanners are programs that detect potential vulnerabilities in an organization’s network. They detect security holes in a system and alert network administrators when they are found. A vulnerability scan is often limited, however, by its ability to identify only known vulnerabilities. Modern systems change frequently, so a scan is only a snapshot of what is known at the time of the scan.
Many vulnerability scanners are free and do not require any special knowledge or expertise. They will search your network for thousands of vulnerabilities, including missing patches, vulnerable services, unsafe default configurations, and web applications. Some vulnerability scanners can find several vulnerabilities in a single scan, and the reports will give you the details you need to resolve them.
While a vulnerability scanner can find thousands of vulnerabilities, it is important to remember that it can’t detect every potential flaw. A single vulnerability can enable an attacker to breach a network. Performing internal and external vulnerability scans at least quarterly will help to ensure your organization’s security is up to date.
Vulnerability scanners work by scanning network resources, such as ports and applications, and then generating reports about any vulnerabilities they find. This process uses two mechanisms: the sounding mechanism, which can launch and monitor attacks, and the probing mechanism, which confirms possible directions of attack. In the end, it helps identify vulnerabilities and prevent the spread of harmful software.
How Do Vulnerability Scanners Work?
Vulnerability scanners are crucial tools in cybersecurity. They help organizations identify vulnerabilities early and prioritize remediation measures. They can also help identify unauthorized devices and other indications that systems may be compromised. They can also pinpoint what operating system and firmware updates were updated recently, and when they were last patched. Unpatched vulnerabilities are the cause of many data breaches and security gaps. Therefore, it is vital to eliminate all potential security holes and make your IT ecosystem more secure.
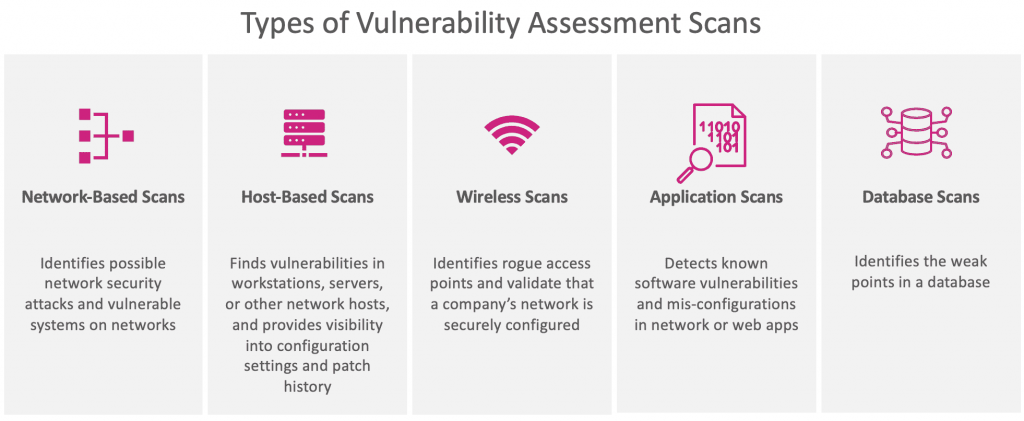
Vulnerability scanners have two main types: network based and endpoint scanners. Internal scanners probe your internal network and determine which systems are exposed to the internet. They are similar to external scanners, but have different goals. Internal scanners find vulnerabilities in the organization’s network, while external scanners identify vulnerabilities in web applications and open services. Internal scanners can be less comprehensive, but are still an important step in network security.
Some of the best vulnerability scanners are open source, so you need to make sure you’re using one that supports the open source model. An open source code vulnerability scanner will be able to detect issues before they are exploited, identifying affected instances and locking out attackers. An open source code vulnerability scanner will also document any open-source frameworks and libraries used in your application, ensuring that your software complies with the open-source license.
While it may be tempting to go with the first vulnerability scanner you come across, it may not be the best option for your needs. A good vulnerability scanner should have a simple interface that allows you to easily navigate the process of vulnerability scanning. For example, you can use a tool like MaxPatrol to identify vulnerable files on your system. This program has a convenient interface that displays the different stages of network security scanner work. Its menus display links for a vulnerability, a service, and a node.

